Introduction to Agave House
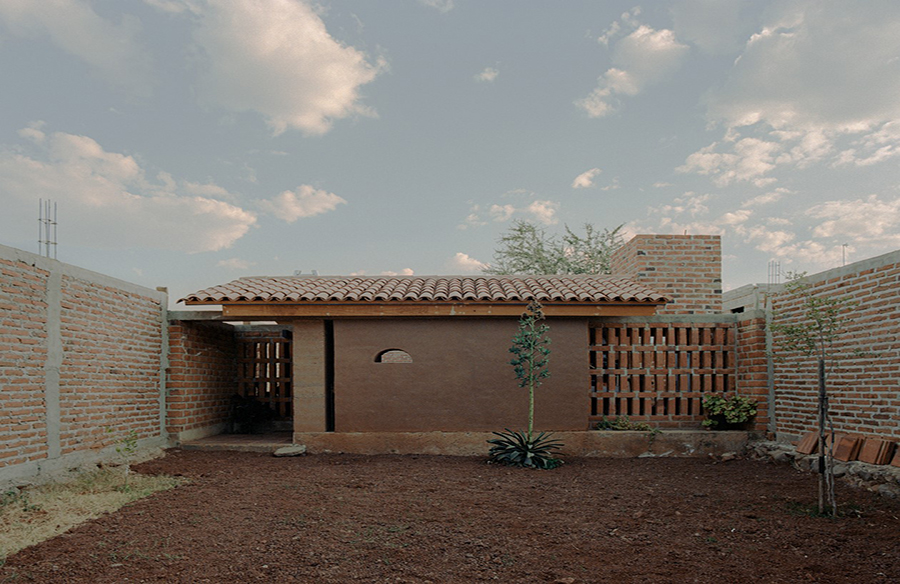
Located in the heart of Tequila, Jalisco, a region renowned for its tequila industry and growing tourism, Agave House embodies a unique architectural response to the rapid urban development characterized by industrial materials and high energy consumption. This project reclaims the identity of one of Mexico’s most iconic towns through thoughtful design and material choice, preserving the essence of its agave landscape.
Material Innovation
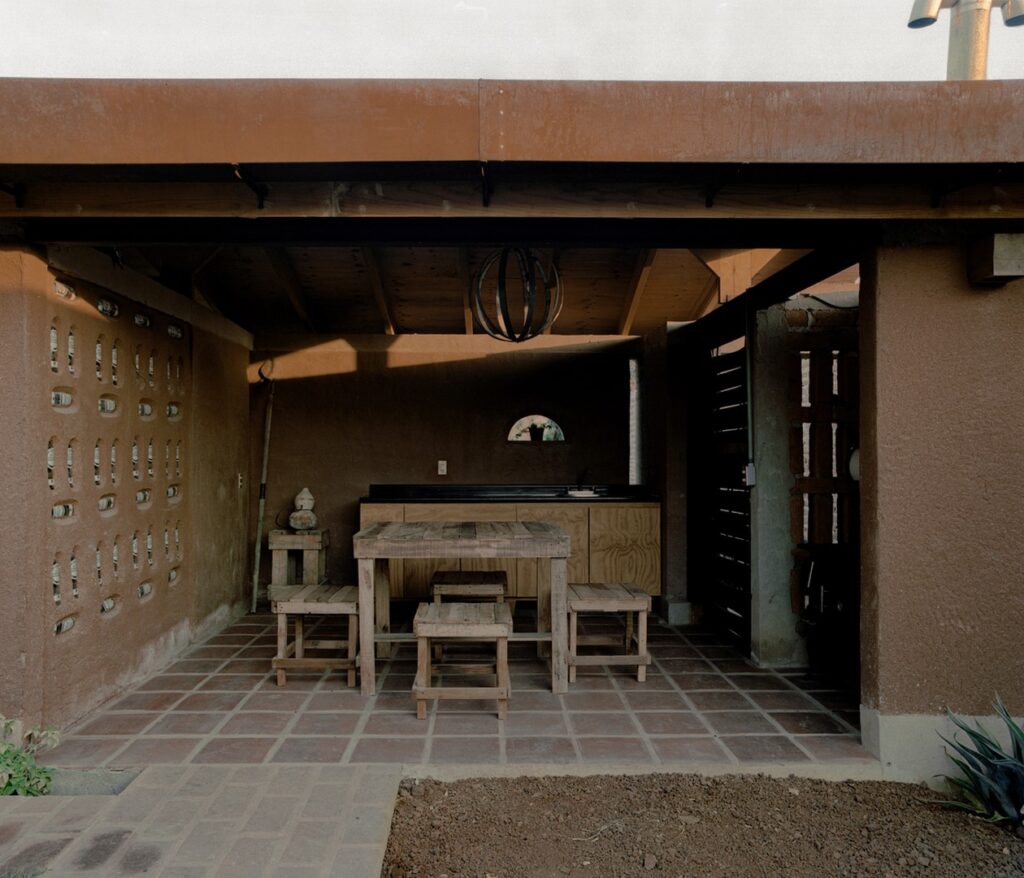
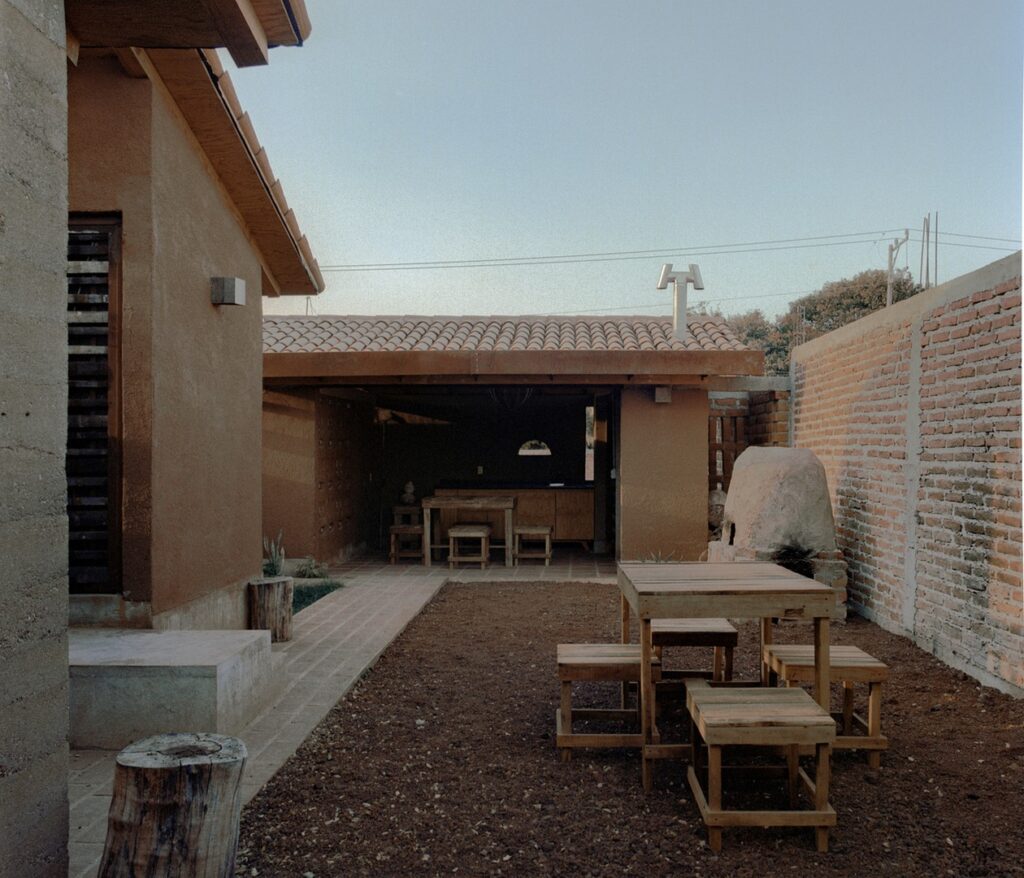
Agave House leverages materials derived from the tequila industry for various construction elements, including walls, finishes, furniture, doors, lighting, floors, and stained glass windows. This approach ensures the house is deeply rooted in the local culture and environment. The use of these materials not only reduces environmental impact but also highlights the distinctive color palette and textures of the region.
Bioclimatic Design
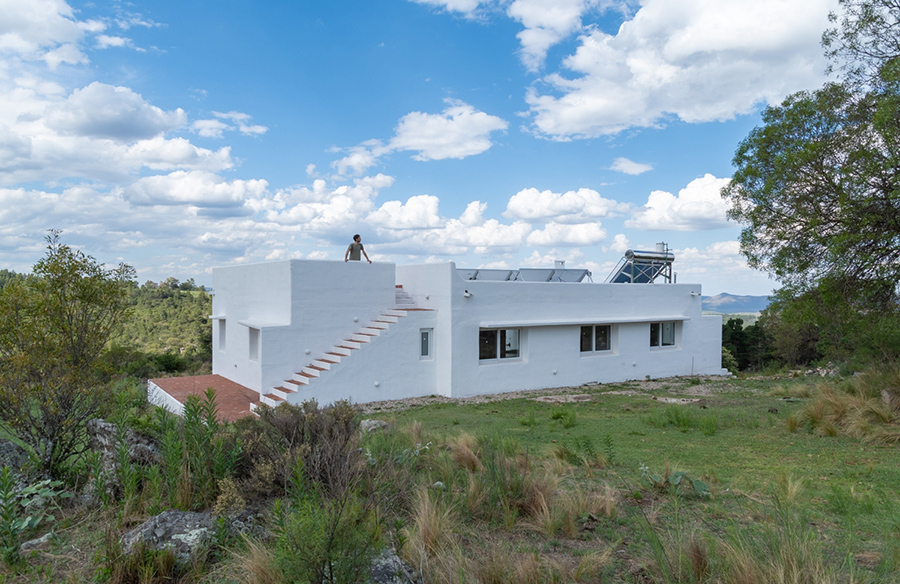
The design of Agave House considers several critical factors such as the land’s natural characteristics, sun orientation, climate, and topography. By integrating bioclimatic principles, the house benefits from cross ventilation and natural lighting, enhancing comfort and reducing energy consumption. The sloping roofs and traditional tiles further anchor the house in its local context while meeting modern sustainability criteria.
Community Involvement and Education
The construction process of Agave House served as an educational platform for local residents and students, fostering interest in sustainable building practices. By involving the community, the project not only disseminated knowledge about eco-friendly construction but also encouraged the adoption of these practices more broadly.
Eco-Technologies Incorporated
Agave House incorporates several eco-technologies to minimize its environmental footprint:
- Dry Toilet: This waterless toilet system prevents pollution, waste generation, and odors, converting waste into compost.
- Wood Stove and Oven: Utilizing firewood, this eco-technology reduces reliance on natural gas, a non-renewable resource.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Equipped with a Tláloc type water filter and a 5000-liter storage cistern, the house collects and stores rainwater for various uses.
- Electric Boiler: Providing hot water without burning hydrocarbons or other fuels, this boiler contributes to the house’s overall energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Agave House stands as a model of sustainable architecture, blending traditional Mexican elements with modern eco-technologies. Through the use of locally sourced materials and bioclimatic design principles, it preserves the cultural identity of Tequila while promoting environmental stewardship and community education. This project exemplifies how architecture can honor heritage and embrace sustainability, offering a blueprint for future developments in the region.